Antwort What is an example of ecological economics? Weitere Antworten – What is ecological economics in simple words
Ecological economics is distinguishable from neoclassical economics primarily by its assertion that the economy is embedded within an environmental system. Ecology deals with the energy and matter transactions of life and the Earth, and the human economy is by definition contained within this system.The three interrelated goals of ecological economics are sustainable scale, fair distribution, and efficient allocation. All three of these contribute to human well-being and sustainability. Distribution has many different impacts, not the least of which is its impact on social capital and on quality of life.The authors distill four fundamental principles for ecological economics based on systems theory of life and philosophy of organism. The four principles are; nested systems, self-generating networks, open systems, and cognitive interactions.
What is the field of ecological economics : Ecological economics is a new and growing multi-disciplinary field of endeavor that seeks the expansion and improvement of existing economic theory to include natural systems of the earth, human health, values, and their well-being (Czech, 2009; Martinez-Alier, 1998).
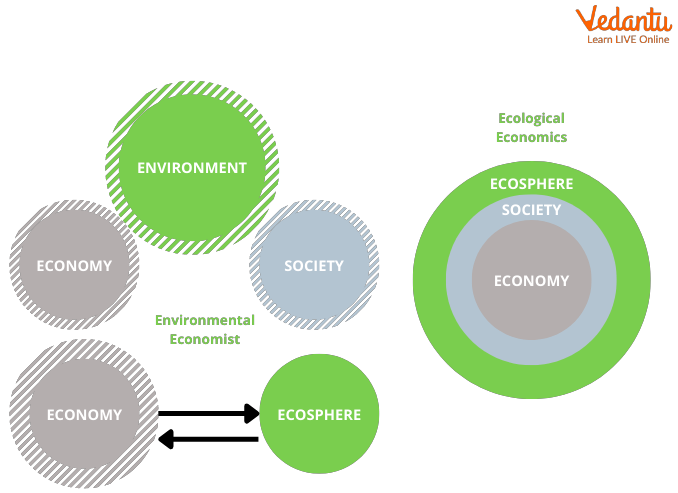
What is the difference between environmental and ecological economics
The difference is that environmental economics studies the relationship between the environment and the economy, while ecological economics considers the economy to be a subsystem of the wider ecosystem.
What are the approaches to ecological economics : The major conceptual issues emerging in the ecological economics literature are value monism, the rational actor model, marginal analysis, the treatment of uncertainty, the role of efficiency in economic policy, and production as a social and physical process.
What are examples of ecology Examples of ecological interactions include energy movement through food webs, symbiotic relationships among different species, and resource competition that limits the survival of certain species.
The main concepts of ecology are ecosystems., biosphere, organism, population and community. At the organization stage, Ecologists study the relationships between specific organisms and the immediate environment.
Where can I study ecological economics
UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAMS
- UC Berkeley: Environmental Economics and Policy.
- University of Maryland: Agricultural and Resource Economics.
- Sarah Lawrence: Environmental Studies.
- Michigan State University: Environmental Economics and Management.
- Temple University – Environmental Studies, College of Liberal Arts.
Green economics is closely related to ecological economics but is different because it is a holistic approach that includes political advocacy of sustainable solutions. Some critics believe that "green" economic solutions are counterproductive, due to unexpected impacts on the natural environment.Whilst environmental economists are concerned with the efficient allocation of natural resources, ecological economists figure out the cost-benefit of preserving or protecting natural resources.
Whilst environmental economists are concerned with the efficient allocation of natural resources, ecological economists figure out the cost-benefit of preserving or protecting natural resources.
What is a good example of ecology : Examples include deserts, grasslands, tundras, tropical rainforests, and temperate forests. A population is a group of organisms of the same species that interact regularly with one another. Biodiversity is a broad term for the variety of species found in a particular habitat or ecosystem (or other unit of area).
What is the best example of ecology : What are examples of ecology Examples of ecological interactions include energy movement through food webs, symbiotic relationships among different species, and resource competition that limits the survival of certain species.
What are the 7 types of ecology
Listed below are the types:
- Aquatic Ecology. It deals with the study of ecosystems found in water bodies such as estuarine, freshwater and marine.
- Microbial Ecology.
- Terrestrial Ecology.
- Taxonomic Ecology.
- Systems Ecology.
- Evolutionary Ecology.
- Behavioural Ecology.
- Population Ecology.
The Ten Principles of Ecology
- Evolution organizes ecological systems into hierarchies.
- The sun is the ultimate source of energy for most ecosystems.
- Organisms are chemical machines that run on energy.
- Chemical nutrients cycle repeatedly while energy flows through an ecosystem.
- dN/dt=B-X+I.
- dS/dt=D-X+I.
With this degree, you will have a set of skills in theory, quantitative methods, and communication that are highly sought by employers in government, non-profits, and private industry. An Environmental Economics and Policy degree also provides an excellent foundation on which to apply graduate school.
Where do environmental economists work : Many environmental economists work for the government, either in federal or state-run institutions. These professionals most often work on projects like reviewing existing environmental and economic policies and implementing new ones.